Level of need
Prevalence of drug misuse
Prevalence estimates for drug use in the population are available for opiate and/or crack users (OCUs) specifically, in the 15-64 populations. For North Tyneside the prevalence rate of 977 per 100,000 for this group. This is similar to the picture at a national level, with the rate for England estimated to be 954 per 100,000. However, regionally the North East is higher than national figures, with the rate estimated at 1340 per 100,000.
Drug related Harm
Adult drug specific hospital admissions in North Tyneside are higher than both regional and national figures. Data from 2021-22 shows that the rate for North Tyneside is 93.2 per 100,000 (from OHID. 2024. Adult Drug Commissioning Support Pack: 2023-24: Key Data). The rate of hospital admissions due to substance misuse for 15-24 year olds is 179 per 100,000, again over double the England rate of 81 per 100,000.
In England, for 2021-2023, the rate of drug misuse deaths sits at 12.9 per 100,000 and has increased from previously recorded data. Regionally, the North East continues to have the highest rates in the country at a rate of 9.8 per 100,000 for 2021-23. This data shows that North Tyneside have the third highest rate for drug misuse deaths in the North East, of 12.9 per 100,000.
Toxicology results obtained from Northumbria Police show, for 2023, the top contributory drug types for drug misuse deaths in North Tyneside were both pregabalin and cocaine. The top contributory drugs are those that show up on the most toxicology reports for drug misuse deaths in North Tyneside. This does not necessarily indicate that these drugs were the cause of death, but that they were in the system at time of death. New trends show taking specific drugs, such as pregabalin, alongside heroin or morphine, may increase the risk of an overdose. For suspected intentional overdoses for the same year cocaine was the top contributing drug. This has changed from recent years when Diazepam has been top.
Treatment Services
There are a number of ways a person can be referred to drug treatment services in North Tyneside. Figure 2 shows these different routes and the proportion of new presentations for each one. North Tyneside largely follow the same trend as the national picture, the highest number of new presentations to treatment are via self-referral, with 51% of service users following this route.
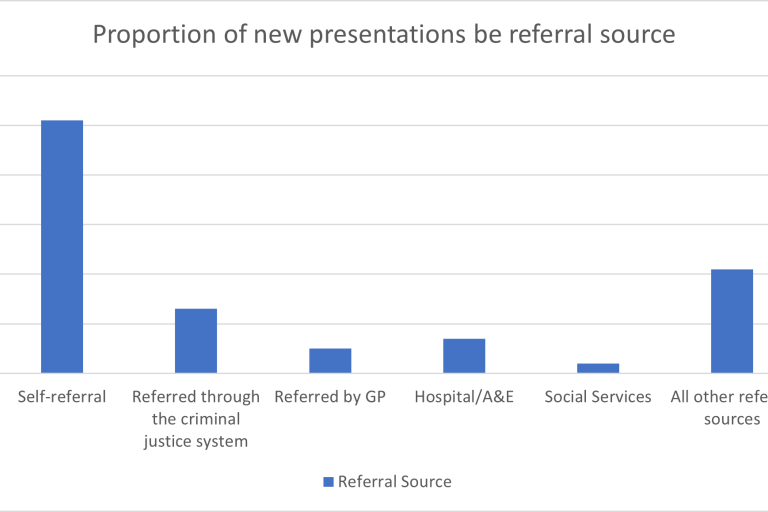
Source: OHID Commissioning Support Pack
In North Tyneside, the number of adults engaged with treatment services in 2021-22 was 1032, 41% of these were a new presentation to treatment. Of those in contact with treatment services, 68% were male and 32% female (from OHID. 2024. Adult Drug Commissioning Support Pack: 2023-24: Key Data). This split is similar to the national picture of 71% male, 29% female. The most sited substance of all adults in treatment in North Tyneside was Cocaine, with 38% of the treatment population naming this.
The number of young people in treatment, including young adults in young people’s services for North Tyneside in 2022-23 was 146, with 60% of them being male. This figure includes under 18s and 18-24s in young people treatment, it does not include 18-24s in contact with adult substance misuse services (from:OHID. 2024. Young people substance misuse commissioning support park: 2022-23: Key Data).
Vulnerable Groups
Drug misuse can occur frequently among people with poor mental health, with research indicating up to 70% of people in community substance misuse treatment nationally, also experience mental illness10. Data from treatment services shows that in North Tyneside 71% of adult clients on new treatment journeys, in the year 2021/22, had mental health needs identified, which is a significant increase from the previous year7. In young people, 59% of those new to treatment were identified as having a mental health treatment need (from:OHID. 2024. Young people substance misuse commissioning support park: 2022-23: Key Data)
Drug misuse can occur frequently among people with poor mental health, with research indicating up to 70% of people in community substance misuse treatment nationally, also experience mental illness10. Data from treatment services shows that in North Tyneside 71% of adult clients on new treatment journeys, in the year 2021/22, had mental health needs identified, which is a significant increase from the previous year. In young people, 59% of those new to treatment were identified as having a mental health treatment need (from:OHID. 2024. Young people substance misuse commissioning support park: 2022-23: Key Data).
68% of clients in treatment in North Tyneside are male, matching what is seen at a national level of those who misuse drugs7. In North Tyneside the age groups with the highest numbers in treatment, and potential higher levels of need, are 30-39, with 36% of service users in this category, and 40-49, with 29% (from: OHID. 2024. Adult Drug Commissioning Support Pack: 2023-24: Key Data).
Children of parents or carers who use drugs are a group of the population more vulnerable, or at risk of using drugs. From the new adult presentations to treatment 2021/22, 16% of adults stated they were parents living with children and 21% were parents not living with children.
Another vulnerable group identified at risk by NICE, is those not in employment, education of training. In 2021/22, 56% of adults were unemployed at the start of drug treatment and 56% of young people were not in education, employment or training.
68% of clients in treatment in North Tyneside are male, matching what is seen at a national level of those who misuse drugs. In North Tyneside the age groups with the highest numbers in treatment, and potential higher levels of need, are 30-39, with 36% of service users in this category, and 40-49, with 29% (from:OHID. 2024. Adult Drug Commissioning Support Pack: 2023-24: Key Data).
Children of parents or carers who use drugs are a group of the population more vulnerable, or at risk of using drugs. From the new adult presentations to treatment 2021/22, 16% of adults stated they were parents living with children and 21% were parents not living with children.
Another vulnerable group identified at risk by NICE, is those not in employment, education of training. In 2021/22, 56% of adults were unemployed at the start of drug treatment and 56% of young people were not in education, employment or training.
